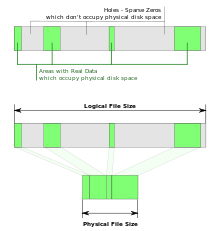
A sparse file: The empty bytes don't need to be saved, thus they can be represented by
metadata.
In computer science, a sparse file is a type of computer file that attempts to use file system space more efficiently when blocks allocated to the file are mostly empty. This is achieved by writing brief information (metadata) representing the empty blocks to disk instead of the actual "empty" space which makes up the block, using less disk space. The full block size is written to disk as the actual size only when the block contains "real" (non-empty) data.
When reading sparse files, the file system transparently converts metadata representing empty blocks into "real" blocks filled with zero bytes at runtime. The application is unaware of this conversion.
Most modern file systems support sparse files, including most Unix variants and NTFS.[1] Apple's HFS+ does not provide for sparse files, but in OS X, the VFS layer supports storing them in any supported file system, including HFS+. Sparse files are commonly used for disk images, databasesnapshots, log files and in scientific applications.
Contents
-
1 Advantages
-
2 Disadvantages
-
3 Sparse files in Unix
-
3.1 Creation
-
3.2 Detection
-
3.3 Copying
-
3.4 Piping
-
4 See also
-
5 References
-
6 External links
Advantages
The advantage of sparse files is that storage is only allocated when actually needed: disk space is saved, and large files can be created even if there is insufficient free space on the file system. This also reduces the time of the first write as the system doesn't have to allocate blocks for the "skipped" space. Since initial allocation usually requires the system to write all zeros to the space, it also keeps the system from having to write over the "skipped" space twice.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages are that sparse files may become fragmented; file system free space reports may be misleading; filling up file systems containing sparse files can have unexpected effects (such as disk-full or quota-exceeded errors when merely overwriting an existing portion of a file that happened to have been sparse); and copying a sparse file with a program that does not explicitly support them may copy the entire, uncompressed size of the file, including the zero sections which are not allocated on disk—losing the benefits of the sparse property in the file. Sparse files are also not fully supported by all backup software or applications. However, the VFS implementation sidesteps the prior two disadvantages. Loading executables on Windows (exe or dll) which are sparse takes a much longer time, since the file cannot be memory mapped and not cached.
Sparse files in Unix
Sparse files are typically handled transparently to the user. But the differences between a normal file and sparse file become apparent in some situations.
Creation
The Unix command
dd of=sparse-file bs=1k seek=5120 count=0
will create a file of five mebibytes in size, but with no data stored on disk (only metadata). (GNU dd has this behaviour because it calls ftruncate to set the file size; other implementations may merely create an empty file.)
Similarly the truncate command may be used, if available:
truncate -s 5M <filename>
Detection
The -s option of the ls command shows the occupied space in blocks, and -k the apparent size in blocks too:
ls -lks sparse-file
-h can be used to print both in human readable format.
Alternatively, the du command prints the occupied space, while ls prints the apparent size. The option --block-size=1 prints the occupied space in bytes instead of blocks, so that it can be compared to the ls output:
du --block-size=1 sparse-file
ls -l sparse-file
Copying
Normally, the GNU version of cp is good at detecting whether a file is sparse, so
cp sparse-file new-file
creates new-file, which will be sparse. However, GNU cp does have a --sparse=WHEN option.[2] This is especially useful if a file containing long zero blocks is saved in a non-sparse way (i.e. the zero blocks have been written out to disk in full). Disk space can be saved by doing:
cp --sparse=always file1 file1_sparsed
Some cp implementations, like FreeBSD's cp, do not support the --sparse option and will always expand sparse files. A partially viable alternative on those systems is to use rsync with its own--sparse option[3] instead of cp. Unfortunately --sparse cannot be combined with --inplace, so rsyncing huge files across the network will always be wasteful of either network bandwidth or disk bandwidth.[citation needed]
Piping
cat somefile | cp --sparse=always /proc/self/fd/0 new-sparse-file